As AI rapidly transforms business landscapes, driving efficiency and innovation, it also introduces critical challenges around ethical AI, responsible AI, and AI compliance. With the surge in AI deployment across industries, organizations must adopt robust AI governance frameworks to ensure ethical, transparent, and accountable AI practices. Lacking governance, issues like AI bias, privacy risks, and regulatory non-compliance threaten both brand reputation and operational integrity.
This article equips business leaders with an understanding of AI governance, from key components to implementation strategies, enabling organizations to manage AI risk effectively while fostering trust and aligning with AI regulatory standards.
What is AI Governance?
AI governance is a structured framework designed to ensure the ethical and responsible use of AI within an organization. As businesses increasingly rely on AI to drive efficiency and innovation, AI governance becomes essential for aligning AI applications with corporate values, regulatory standards, and societal expectations. This governance framework encompasses policies, processes, and oversight mechanisms that help organizations manage AI risk, enhance AI transparency, and support compliance with AI ethics.
Core Objectives of AI Governance
- Ensuring Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency: AI governance aims to mitigate AI bias and promote AI fairness by monitoring algorithms and data sets for unintended discrimination. It also ensures transparency in AI decisions, making them explainable and accountable to both users and stakeholders.
- Aligning AI with Corporate Values and Regulatory Compliance: AI governance frameworks help align AI initiatives with a company’s values, supporting ethical AI use. They also ensure adherence to AI compliance standards, addressing regulatory requirements in data privacy, security, and risk management.
- Mitigating Risks Related to Bias, Privacy, and Ethical Misuse: Governance frameworks actively address AI risk by implementing AI bias mitigation strategies, enhancing AI transparency tools, and securing data privacy. These steps protect against unethical AI deployment and safeguard an organization’s reputation.
By embedding AI governance best practices into business operations, organizations create a responsible AI strategy that builds trust, supports compliance, and unlocks the benefits of AI in a secure, transparent way.
Why AI Governance is Essential for Today’s Business Landscape
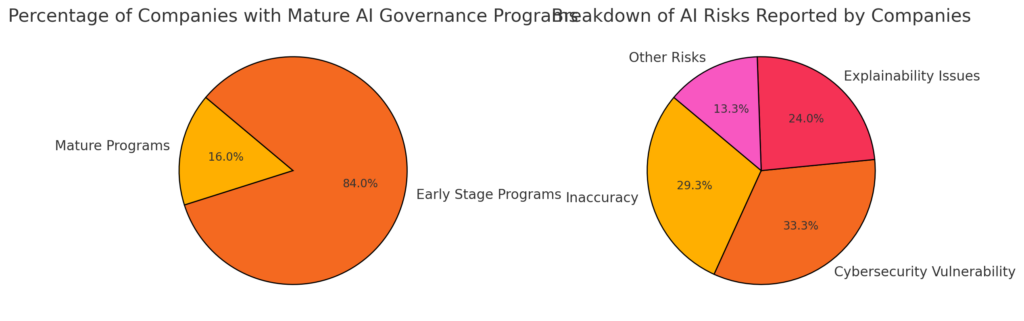
As AI becomes more integral to business operations, its governance is critical. Surprisingly, only 16% of companies have mature AI governance programs, despite 84% of executives recognizing responsible AI as a top management priority. This disparity highlights the urgency for businesses to prioritize robust governance structures. (KPMG)
For companies investing in responsible AI, the rewards are significant—50% higher revenue growth and improved customer trust, positioning responsible AI as a strategic advantage. (Accenture) Effective AI governance, therefore, is not only essential for compliance but also fosters competitive differentiation and builds consumer confidence in the AI-driven future.
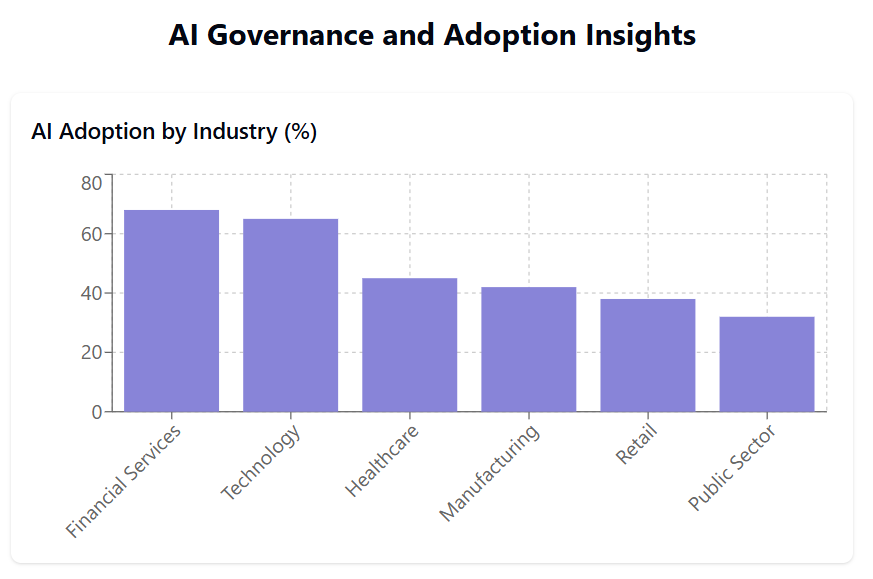
1. Building Trust and Accountability
Governance frameworks help organizations establish credibility and trust by fostering transparency and accountability in AI-driven decisions. Here’s how:
- Transparency in AI Decisions: Imagine a financial institution using AI to assess loan applications. If the decision-making process is opaque, it can lead to customer skepticism and regulatory scrutiny. AI governance encourages transparency by ensuring decisions can be explained, which reassures stakeholders and builds trust.
- Creating Accountability Structures: Governance frameworks often establish AI ethics boards and compliance teams to oversee AI practices, adding a layer of accountability. For example, Google’s AI Principles include a board to monitor its AI projects and ensure alignment with ethical standards, demonstrating commitment to responsible AI use.
2. Compliance with Global Regulations
The global regulatory landscape for AI is rapidly evolving. As AI becomes more integral to business operations, compliance with AI regulations is no longer optional; it’s a strategic necessity.
- Navigating Emerging AI Regulations: New laws such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the proposed EU AI Act enforce strict guidelines on data privacy and ethical AI practices. For instance, GDPR mandates that companies protect personal data used in AI models, while the EU AI Act classifies AI systems based on their risk level, with higher-risk applications facing tighter regulations.
- The Business Impact of Compliance: Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and damage to brand reputation. For instance, non-compliance with GDPR can result in penalties up to 4% of annual global revenue. By proactively adhering to these AI compliance standards, companies minimize legal risks and avoid disruptions that may arise from regulatory challenges.
3. Protecting Brand Reputation
AI-related missteps can significantly harm a company’s reputation and erode consumer trust. Governance frameworks protect brand reputation by embedding ethical AI practices and risk mitigation strategies into AI development.
- Mitigating Risks of AI Missteps: Let’s take a high-profile example: in 2018, Amazon discontinued its AI hiring tool after discovering it was biased against women. This instance highlighted the risks of unchecked AI bias and the importance of having AI governance in place to prevent reputational damage.
- Embedding AI Bias Mitigation: Governance frameworks emphasize bias testing and mitigation, particularly in sensitive areas like hiring, finance, and healthcare. For instance, IBM’s AI Fairness 360 toolkit provides bias detection tools to help organizations develop fairer AI models, reducing the risk of public backlash from biased outcomes.
Key Components of Effective AI Governance
An effective AI governance framework addresses transparency, data privacy, and risk management, but achieving these components is challenging. According to McKinsey, 44% of companies have experienced negative outcomes from AI inaccuracies, and nearly half cite cybersecurity and explainability as ongoing risks (MCKINSEY & COMPANY).
Despite these risks, only 62% of organizations have an AI governance framework, and even fewer (47%) have implemented risk management protocols (Accenture). Including these risk management practices, such as transparency tools and data privacy safeguards, is crucial for mitigating the significant risks associated with AI.
1. Ethics and Bias Mitigation
Ethical principles like fairness, transparency, and empathy are foundational to AI governance.
- Guiding Ethical Principles:
- Fairness: Ensures AI systems provide equal treatment and avoid discrimination.
- Transparency: Makes AI processes open and understandable.
- Empathy: Considers the impact of AI decisions on individuals and society.
- Bias Detection and Mitigation Strategies:
- Regularly monitor data and models for biases (e.g., demographic biases in hiring tools).
- Use bias detection tools like IBM’s AI Fairness 360 to evaluate and reduce biases in AI algorithms.
- Implement diverse data sources and testing with varied demographics to ensure fair outcomes across all user groups.
Example: A financial firm using AI for loan approvals can mitigate potential bias by analyzing historical loan data for demographic fairness, ensuring the model doesn’t favor one group over another.
2. Transparency and Explainability
Transparency in AI systems is essential to build trust with users, regulators, and stakeholders.
- Why Transparency Matters:
- Transparency allows end-users to understand how and why AI makes decisions, which is critical for AI trustworthiness.
- By making AI processes explainable, companies foster accountability and enhance consumer confidence.
- Tools and Methods for Explainability:
- SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations): Provides visual explanations of individual predictions, helping users understand feature impact on decisions.
- LIME (Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations): Breaks down complex models into simpler explanations for end-users.
Example: A healthcare AI model providing treatment recommendations can use SHAP to visually explain its decisions to doctors, making it easier for them to trust and validate AI-generated suggestions.
3. Privacy and Data Protection
Privacy safeguards, such as GDPR and CCPA, are critical in AI governance.
- Data Protection Standards:
- GDPR: Ensures personal data used in AI complies with strict privacy standards.
- CCPA: Protects data privacy rights in California, covering data access, deletion, and sharing.
- Privacy Techniques:
- Anonymization: Removes identifying details from data to protect privacy.
- Data Minimization: Limits data collection to only necessary information, reducing privacy risks.
Example: An AI-driven retail recommendation system that anonymizes customer data complies with data protection laws while maintaining personalization.
4. Accountability and Oversight
Oversight roles ensure AI practices align with ethical standards and regulations.
- AI Ethics Boards: Oversee AI projects, ensuring alignment with ethical guidelines.
- Compliance Teams: Verify that AI models adhere to industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- C-Level Involvement: Executive leaders set the tone for AI accountability and cross-functional governance.
- Cross-Functional Governance: Regular audits and cross-functional collaboration (e.g., involving legal, IT, and data science teams) are crucial to enforce AI accountability and maintain governance standards across departments.
Each component collectively strengthens AI governance, helping organizations build fair, transparent, and responsible AI systems.
Implementing AI Governance in an Organization
Establishing AI governance within an organization requires a structured framework, clear policies, and cross-functional collaboration to align AI initiatives with ethical standards and regulatory requirements.
Developing a Governance Framework
Creating a structured AI governance framework aligns AI goals with corporate strategy and integrates AI governance best practices across teams.
- Establish Core Objectives: Define AI goals that support corporate values and business objectives, focusing on ethical AI and compliance.
- Assemble Cross-Functional Teams: Include representatives from IT, Legal, Compliance, and Data Science to cover diverse governance areas.
- Assign Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define each team’s role in AI risk management, bias mitigation, and AI compliance.
Setting AI Policies and Standards
Corporate policies form the foundation for responsible AI practices.
| Policy Area | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Data Usage | Set guidelines for ethical data use | Limit data to relevant, unbiased sources |
| Model Accuracy | Establish standards for accuracy levels | Regular testing for reliable predictions |
| Risk Management | Outline AI risk mitigation strategies | Implement safeguards against data breaches |
Training and Stakeholder Engagement
Engage both employees and stakeholders to ensure transparency and a shared commitment to ethical AI.
- Employee Training: Regular workshops on AI ethics, bias detection, and data privacy to equip staff with governance skills.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Keep consumers, regulators, and investors informed about AI practices, enhancing AI transparency and building trust.
This multi-layered approach ensures that AI governance aligns with business goals, supports ethical standards, and fosters accountability across the organization.
Key Challenges in AI Governance and How to Overcome Them
Implementing AI governance poses challenges like balancing innovation with compliance, managing data securely, and adapting to evolving regulations. Addressing these effectively ensures responsible, compliant, and growth-oriented AI practices.
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Balancing Innovation and Regulation | Maintaining compliance without stifling AI innovation. | Develop flexible AI governance frameworks that incorporate compliance standards while allowing room for controlled AI experimentation. |
| Complexity in Implementing AI Ethics | Translating AI ethics guidelines (e.g., fairness, transparency) into actionable steps. | Break down ethical principles into specific, trackable tasks like bias testing. Establish an AI ethics board for regular oversight and review. |
| Data Management | Securing, managing, and curating data while protecting privacy and maintaining data integrity. | Use data anonymization and data minimization for privacy. Implement data governance tools to ensure compliance with standards like GDPR. |
| Evolving Regulations and Standards | Keeping up with the dynamic nature of AI regulations and adapting governance frameworks accordingly. | Regularly update governance policies. Monitor regulatory changes and ensure governance frameworks are adaptable to new compliance requirements. |
Real-World Examples of AI Governance in Action
Leading companies and governments are actively implementing AI governance frameworks, ethics boards, and regulatory standards to ensure ethical, accountable, and compliant AI use. These initiatives set benchmarks for responsible AI practices across industries.
Corporate Case Studies
Top companies lead in AI governance by implementing ethics boards, frameworks, and tools to ensure responsible AI practices.
| Company | Governance Practices |
|---|---|
| IBM | Launched an AI Ethics Board to oversee AI projects and ensure compliance with AI ethics and responsible AI principles. |
| Microsoft | Created a comprehensive AI governance framework focusing on AI transparency, fairness, and bias mitigation across products. |
| Established an AI Principles Committee to assess new AI projects, focusing on safety, accountability, and ethical AI use in areas like data privacy. |
Key Takeaways from Government Regulations
Governments globally are establishing standards to guide ethical and responsible AI deployment.
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| EU’s AI Act | Classifies AI systems by risk, with stricter regulations on high-risk AI applications to ensure AI compliance and protect data privacy. |
| OECD AI Principles | Emphasizes AI transparency, accountability, and ethics in AI deployment, serving as a guideline for responsible AI use worldwide. |
These examples illustrate how both corporations and governments are proactively shaping the AI regulatory landscape and setting a high standard for AI governance best practices across industries.
The Future of AI Governance: Trends and Predictions
The AI regulatory landscape is rapidly evolving. Over 77% of companies are prioritizing AI compliance in response to new standards like the EU AI Act and GDPR (WORLD ECONOMIC FORUM). Additionally, Accenture research shows that companies focusing on responsible AI practices report 53% higher success in customer experience and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) metrics compared to those without structured governance (ACCENTURE).
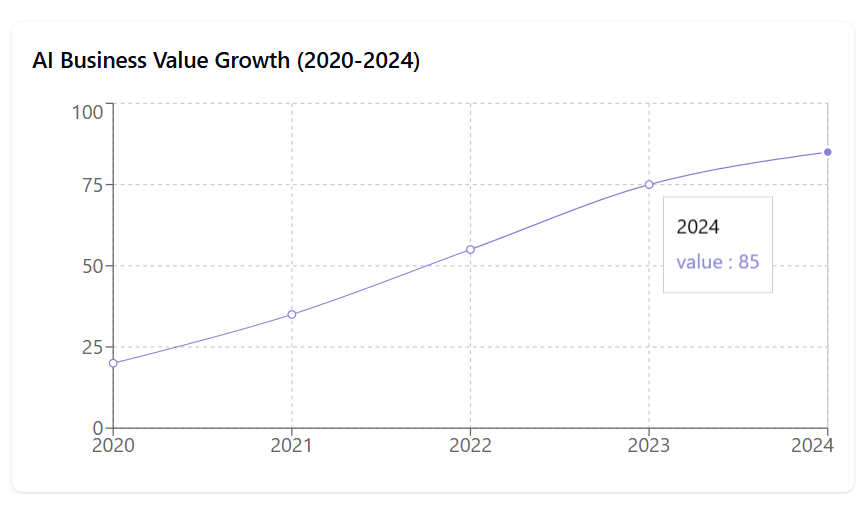
Advanced governance technologies, such as fairness-checking algorithms and compliance automation, will likely play a key role in supporting businesses as regulations grow stricter. These trends point to a future where regulatory readiness and responsible AI use are essential for competitive advantage.
Increasing Regulatory Pressure
Global AI regulations are set to expand, with governments introducing more stringent AI compliance standards and policies to mitigate risks in high-stakes areas like finance, healthcare, and data privacy.
Advanced Governance Technologies
New AI-driven governance tools are on the rise, such as fairness-checking algorithms and compliance automation software that streamline bias detection, transparency, and regulatory adherence.
Toward Human-Centric AI
A growing movement prioritizes ethical AI models that prioritize user rights and societal benefits, aiming to create AI systems that are inclusive, fair, and aligned with public welfare.
Conclusion: Why Business Leaders Should Prioritize AI Governance Today
AI governance is a strategic imperative, not a regulatory formality. With only 16% of companies having mature governance structures, the need for C-suite involvement is critical (KPMG). High-performing organizations, those prioritizing responsible AI, outperform peers in revenue growth and customer experience by as much as 50% (Accenture). Business leaders should take proactive steps to establish or strengthen AI governance frameworks, as these efforts not only reduce risk but also foster trust, compliance, and a sustainable, competitive edge in the AI-driven economy.
- Strategic Importance: Robust governance drives responsible AI growth, reduces AI risk, and ensures ethical AI use.
- C-Suite Involvement: Executive leadership plays a crucial role in ensuring that AI aligns with corporate values and evolving regulatory expectations.
- Call to Action: Business leaders should proactively initiate or strengthen AI governance frameworks to maintain trust, compliance, and a competitive edge in the AI-driven world.
Resources:
https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insights/artificial-intelligence/ai-compliance-competitive-advantage
https://kpmg.com/us/en/board-leadership/articles/2023/acceleration-of-ai-ups-ante-on-governance.html
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2024/09/ai-governance-trends-to-watch/
https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai
